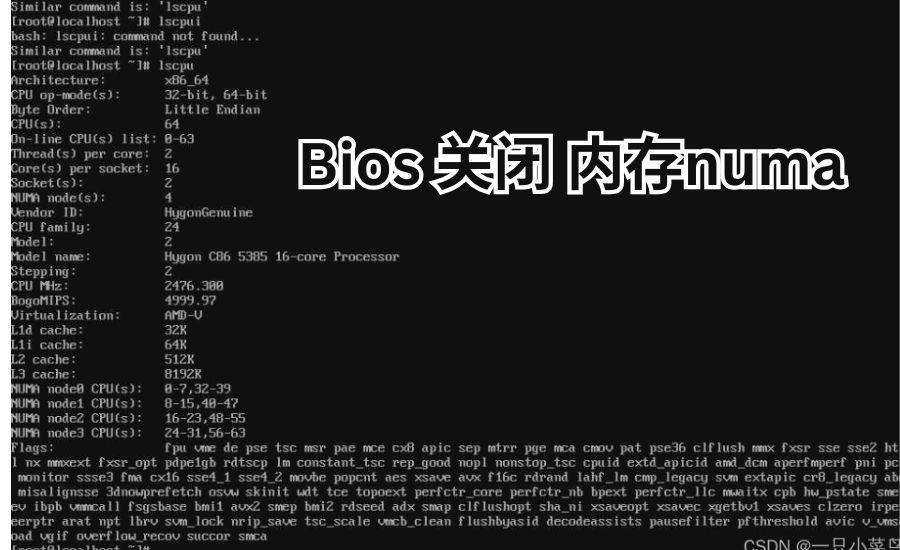
If you’re wondering how to adjust your computer memory settings, BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA might be the solution you need. This feature helps improve how your system uses memory, making it more efficient and balanced.
Many people don’t know how BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA works, but it’s actually quite simple. By turning off NUMA in your BIOS, you can control memory allocation better, especially for older systems or specific tasks. Let’s learn more about this handy feature!
What Does BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA Mean?
When we talk about BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA, we’re referring to a setting in the BIOS that affects how your computer manages memory. NUMA stands for Non-Uniform Memory Access, a way for computers to handle memory more efficiently. When it’s turned off in the BIOS, the laptop manages memory, which can be helpful for specific tasks.
In simple terms, NUMA vs. non-NUMA helps control how your system’s memory is used. Disabling it may speed up your computer, mainly if you use an older machine or specific software that doesn’t need NUMA.
Why Should You Turn Off NUMA in BIOS?
Turning off NUMA in BIOS might improve your computer’s performance in certain situations. For example, when NUMA is on, it can create complex memory pathways that slow down the system. Disabling NUMA helps make these pathways simpler, which can help the computer work faster.
If you are running basic programs or games, you might not need NUMA. Disabling NUMA vs. non-NUMA ensures your memory is used straightforwardly, reducing complexity. This might be especially useful for those who don’t need advanced memory management.
How to Find BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA on Your Computer
Finding NUMA vs. non-NUMA settings can be tricky for some, but it’s not too hard. To start, reboot your computer and enter the BIOS setup by pressing the unique key (usually F2, F10, or DEL) when the computer first turns on. Look for memory or advanced settings once you’re in the BIOS menu.
If you can’t find NUMA vs. non-NUMA, check your motherboard’s manual or the computer’s help guide. Each brand and motherboard may have slightly different names for these settings, but most will include NUMA options in the memory or processor section.
Steps to Adjust BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA Settings
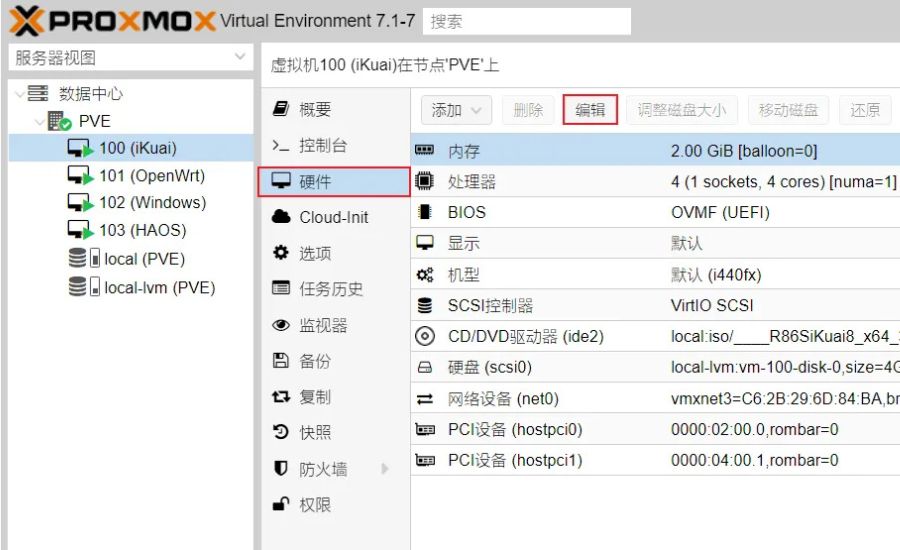
Adjusting BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA settings requires a few simple steps. After entering your BIOS, navigate to the memory or CPU configuration settings using the arrow keys. From there, look for options related to NUMA.
Once you find the NUMA setting, select it and change the value to “Disabled.” Be sure to save your changes before exiting the BIOS. This will disable NUMA and let your system use memory more efficiently, which could improve performance.
Do You Know: Bios-retail-4132-and-4627-xbox-complex
Benefits of Using BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA
Using NUMA configuration can offer several benefits. For example, it can simplify memory management, making the system faster and easier to use. Many older systems don’t need NUMA, so disabling it helps the computer use memory in a more straightforward, more direct way.
By turning off NUMA, your computer can focus on the basics, which is often all that’s needed. This can be especially helpful if you run older software or need more hardware resources.
Common Problems When Using BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA
People might face a few problems when using BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA. One issue is that disabling NUMA can cause specific software programs to behave unexpectedly, as they might rely on NUMA for advanced memory management.
Another problem is that some users may need help navigating the BIOS settings. If the BIOS is set incorrectly, it could cause system instability or crashes. It’s essential to follow the instructions carefully when changing these settings.
Tips for Beginners on BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA
Here are some critical points for beginners on BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA:
- Backup Your Data: Always back up your files before making any changes in BIOS to avoid losing important data.
- Read Instructions: Understand the BIOS settings by checking your computer’s manual or online guides. Each computer may have different options for BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA.
- Go Slow and Be Cautious: Take your time changing settings if you’re unsure what they do. Leave settings as they are if you’re uncertain.
- Test After Changes: After disabling BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA, restart your computer and check its performance. See if there’s an improvement in speed or stability.
- Save Changes: Don’t remember to save any changes you make in the BIOS before exiting. This ensures your adjustments are applied correctly.
- Revert if Needed: If things go wrong after changing BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA, you can always go back into BIOS and reset it to the default settings.
These points will help beginners manage BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA safely and confidently.
Does BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA Work for All Computers?
No, BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA does not work for all computers. Some modern systems are built to take advantage of NUMA, which improves memory performance for more complex tasks. Disabling NUMA on newer systems might actually hurt performance.
However, for older computers or specific simpler setups, BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA can be helpful. It’s essential to check your computer’s specifications to see if NUMA is necessary. If it’s not, turning it off might improve the performance of your computer.
Advanced Tricks for BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA Users
If you’re an advanced user, you might want to experiment with BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA settings to fine-tune your system. One trick is to use performance monitoring tools to see how disabling NUMA affects your computer’s speed.
You can also try different configurations within BIOS to optimize other settings along with BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA. By making minor adjustments, you can get your system to run more efficiently and suit your needs.
What Happens When You Disable NUMA in BIOS?
Disabling BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA will make your system use memory more efficiently. This is usually helpful for basic tasks like web browsing or running older programs. Without NUMA, the system won’t try to manage memory across multiple processors, which can make things faster.
However, disabling NUMA on a newer system with complex tasks could reduce performance. NUMA is often used for high-performance computing, so disabling it on the wrong system might slow things down.
Troubleshooting BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA Issues
Sometimes, BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA can cause problems, like slower performance or system crashes. If you experience issues after disabling NUMA, try resetting the BIOS to default settings. This can help fix any configuration problems that may have happened.
If problems persist, it might be worth checking for BIOS updates. Sometimes, newer versions of BIOS software offer better handling of NUMA and other memory settings.
BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA: Should You Try It?
Whether you should try BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA depends on your needs. If you have an older computer or don’t run memory-heavy programs, disabling NUMA can help improve performance. It’s a simple change; you can always re-enable NUMA if needed.
However, if you have a newer system or need NUMA for complex tasks, it’s better to leave it enabled. Always weigh the pros and cons of changing these settings based on your computer’s needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA is an important setting that can help manage your computer’s memory more efficiently. Turning off NUMA in the BIOS can sometimes improve your computer’s speed, especially if you have an older system. It’s an easy setting to change, but always be careful and follow the instructions closely to avoid any problems.
If you need help deciding whether to disable NUMA, it’s okay to leave it on, especially if your computer is newer or running memory-intensive programs. The key is understanding your system and making the best changes for you. By testing and adjusting BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA, you can fine-tune your computer for better performance.
Read More: Bios-hp-stream-14-ds0003dx-bios
FAQs
Q: What is BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA?
A: BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA is a setting in the BIOS that controls how your computer manages memory. Disabling it simplifies memory management.
Q: Why should I disable NUMA in BIOS?
A: Disabling NUMA can improve speed on older systems or tasks that don’t need complex memory management.
Q: How do I find BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA on my computer?
A: Restart your computer and enter the BIOS settings by pressing the unique key (like F2 or DEL). Look in the memory or CPU settings.
Q: Can disabling BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA slow down my computer?
A: It might slow down newer computers or high-performance tasks because NUMA is designed for complex memory needs.
Q: Will BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA work on all computers?
A: No, it works best for older systems. Newer computers often benefit more from having NUMA enabled.
Q: Is it safe to change BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA?
A: Yes, but following instructions carefully and backing up your data before making changes is essential.
Q: Can I undo changes made to BIOS 关闭 内存NUMA?
A: You can always go back into BIOS and reset the settings to default if needed.